Tendon Laceration
What is a tendon?
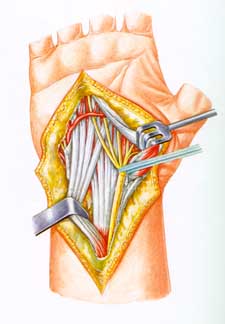
The white, cord-like structures
are the tendons in your wrist that
move your fingers
Tendons are tissues that connect muscles to bone, allowing the force of the muscles to move the joints. A ligament is different, connecting a bone to a bone; its cells are different from the cells of a tendon, so there are other differences besides just what it connects to what. The muscles that move your fingers and thumb are located in your forearm, above your wrist. Long tendons extend from the muscles through the wrist and attach to the small bones of your fingers and thumb. The mucles and tendons that flex your fingers (make a fist) are called flexor muscles and flexor tendons. The ones that open your fist are called extensors. There are many important differences between flexor tendon injuries and extensor tendon injuries.
Anatomy
There are two flexor tendons in each finger, the flexor digitorum superficialis (Latin for finger flexor that is closer to the surface, or superficial), also called the FDS, and the flexor digitorum profundus (Latin for the finger flexor that is deep). The FDP attaches to the last bone of the finger and bends the tip. The FDS bends the middle joint of the finger. They have a very specialized blood supply. Since they move back and forth, they are not connected to the rest of the hand except at certain places, such as the muscle where they come from, the bone where they go, and a specialized structure called the vinculum (Latin for chain or fetter, ie, something that holds something down). The thumb has one tendon. See the pictures below.
The flexor tendons run along the palm side of the fingers and are very close to the surface of the skin, particularly where the skin folds as you bend your fingers. The extensor tendons run along the back side (not the palm side) of your fingers and are also very close to the skin.
If you tear (rupture) or cut (sever) the tendon anywhere along its route—at the wrist, in the palm of the hand, or along the finger, you may be unable to bend your finger. If you injure the FDS tendon, you may still be able to bend the finger, but not completely, and bending the finger will be painful.
Tendons are stretched tightly as they connect the muscle to the bone. If the tendon tears, the end connected to the muscle will be pulled back in toward the palm. Because the tendon can’t heal unless the ends are touching, a severed tendon must be sewn back together again (a surgical repair).
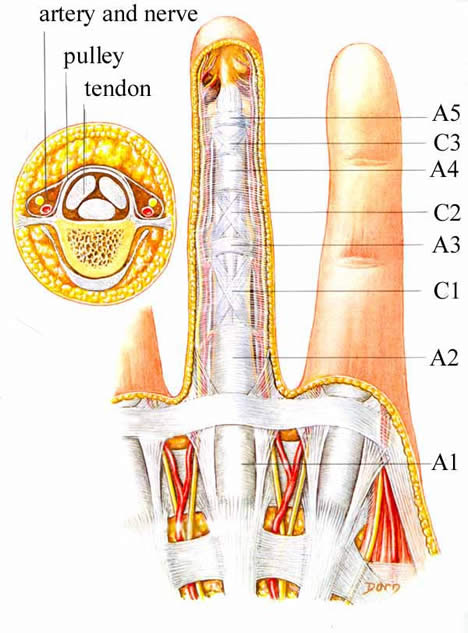
This illustration shows the flexor tendon pulley system (labelled A1 to 5 and C1 to 3). The tendons are below the pulleys, and can be seen in the smaller cross section to the upper left.
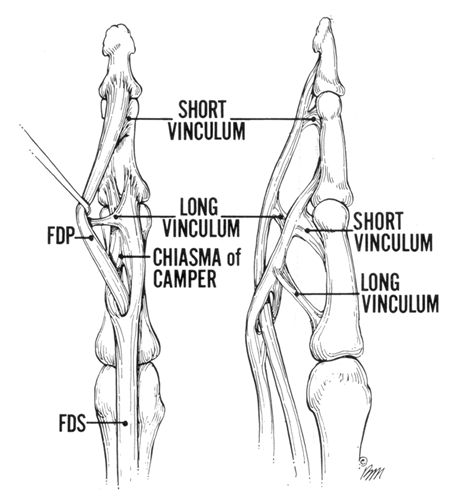
This illustrates the two flexor tendons, the FDP and FDS, as well as their blood supply, that comes through the long and short vincula.
Types of injuries
Most often the flexor tendons are damaged by a cut. Because the nerves to the fingers are also very close to the tendons, a cut may damage them as well, resulting in a feeling of numbness on one or both sides of the finger.
Athletic injuries are also common, usually in football, wrestling or rugby. One player grabs another’s jersey, and a finger—usually the ring finger—gets caught and pulled. This type of injury is so common, it even has a name: "jersey finger." You can also strain or rupture the tendon while rock climbing.
People with rheumatoid arthritis may experience a spontaneous rupture of the flexor tendons. You may notice that the finger no longer bends, but cannot recall when you lost the ability to bend it.
Signs and symptoms of a cut tendon
- An inability to bend one or more joints of the finger
- Pain when you bend your finger An open injury, such as a cut, on the palm side of the hand, particularly in the joint area where the skin folds as the finger bends
- Mild swelling over the joint closest to your fingertip
- Tenderness along the finger on the palm side of the hand
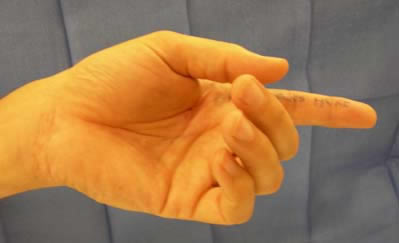 |
| Notice how in this photograph, the index finger is completely straight. Compare this to your own hand at rest. The index finger is usually just gently flexed, a little at all three joints. The above index finger has both tendons cut. (Also notice, the patient has written "this finger" on his finger; all patient are required to mark the operative site. See Preoperative Instructions, instruction #2.) |
Diagnosing your injury
Give me a call if you injure your fingers, especially if you cut your finger or "jam" it and notice that you cannot bend or straighten the tip. For immediate first aid, apply ice and compression to slow the flow of blood to the damaged site.
In the office, I will ask you to bend and straighten the fingers and may apply resistance to test the strength of the fingers. I may also test the sensation and blood flow to your fingers to see if any nerves or blood vessels were also injured. You may need to get an xray to see if there is any damage to the bone; if you have an open wound, you may need a tetanus shot or antibiotics.
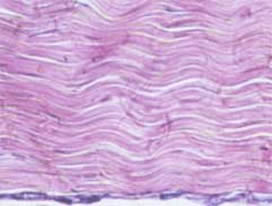 |
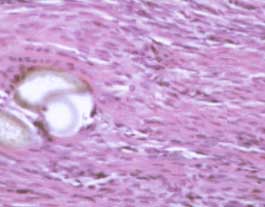 |
| Microscopic view of a normal tendon; the wavy pink material is the collagen bundles; note that there are very few cells. | Microscopic view of a tendon undergoing healing; the white area to the left is the suture; note the increased number of cells. |
Treatment
I may first clean and treat any superficial wounds and put your hand in a splint. Flexor tendon injuries require surgical repair and it’s best to have the surgery soon after the injury, but "soon" here can mean within a week to four weeks. I will sew the tendon together using special stitches on both the inside and outside of the tendon. It can take up to two months before the repair is healed and strong enough to use your hand without protection. It may take another month or so before you can use your hand with any force.
In the meantime, you will need to wear a splint and see a certified hand therapist. The therapist will give you special exercises to perform. Follow my instructions and that of the therapist carefully to ensure the best possible result. This means both preventing adhesions, which will bind the tendon down and prevent you from moving your finger, and a tendon repair rupture, which is the worst of all, since you are back to square one.
Results
The results after surgery depend on many factors: the location and nature of your injury, the delay between injury and first seeing a doctor, the difficulty of the repair and the skill of the surgeon, and (very importantly) how well you cooperate with post-operative hand therapy. The incisions usually heal without much problem. You will experience some stiffness in your finger, but it will improve over a period of two years, and you can dramatically decrease the stiffness by working on range of motion exercises that will be given to you by the hand therapist. You will almost certainly have use of your hand, and probably you have a very good chance of nearly normal use of your hand. The results depend on many variables. I will discuss your particular case with you at the time of the first visit, after the surgery, and as you progress through your rehabilitation.
If you are considering having surgery, you should check out what my patients have written about their experience with tendon surgery.
If you would like to see some pictures of an actual tendon surgery, Case 1, Case 2, Case 3.
~ This page was written by Dr. Nelson, loosely based in part on material prepared by the AAOS. Only Dr. Nelson is responsible for its contents.
